
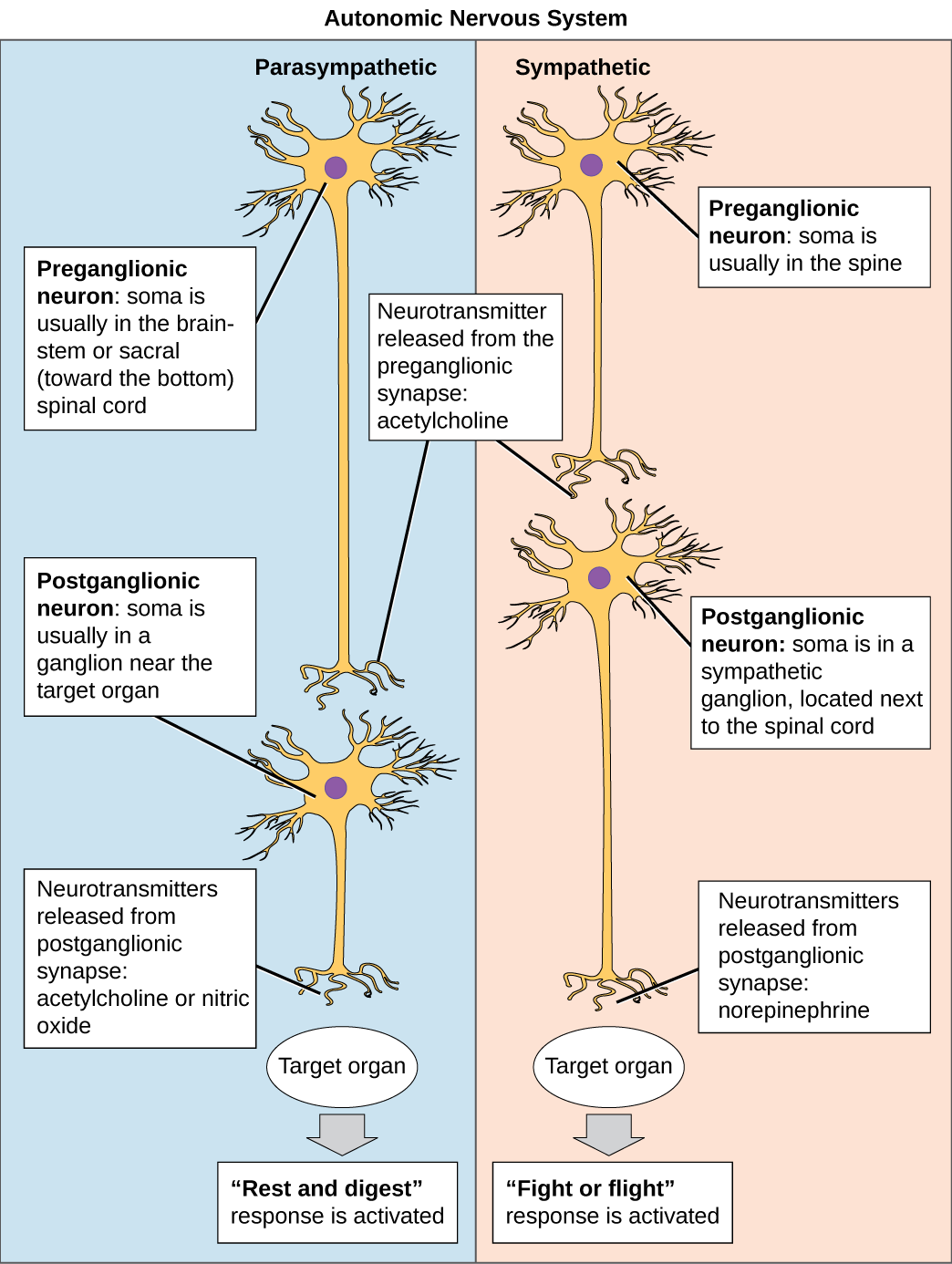
The sympathetic nervous system extends from the thoracic to lumbar vertebrae and has connections with the thoracic, abdominal, and pelvic plexuses. Dopamine is the immediate metabolic precursor to norepinephrine, but is nonetheless a distinct signaling molecule. Postganglionic sympathetic nerves terminating in the kidney release dopamine, which acts on dopamine D1 receptors of blood vessels to control how much blood the kidney filters.The synthesis and release of epinephrine as opposed to norepinephrine is another distinguishing feature of chromaffin cells compared to postganglionic sympathetic neurons. Within this endocrine gland, pre-ganglionic neurons synapse with chromaffin cells, triggering the release of two transmitters: a small proportion of norepinephrine, and more substantially, epinephrine. Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla are analogous to post-ganglionic neurons the adrenal medulla develops in tandem with the sympathetic nervous system and acts as a modified sympathetic ganglion.
#THE SOMATIC NERVOUS SYSTEM IS SKIN#
This leads to the activation of sudomotor function which is assessed by electrochemical skin conductance.
However, there are three important exceptions: The activation of target tissue receptors causes the effects associated with the sympathetic system. In response to this stimulus, the postganglionic neurons release norepinephrine, which activates adrenergic receptors that are present on the peripheral target tissues.
Īt the synapses within the ganglia, preganglionic neurons release acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that activates nicotinic acetylcholine receptors on postganglionic neurons. From there, the long postganglionic neurons extend across most of the body. The shorter preganglionic neurons originate in the thoracolumbar division of the spinal cord specifically at T1 to L2~元, and travel to a ganglion, often one of the paravertebral ganglia, where they synapse with a postganglionic neuron. There are two kinds of neurons involved in the transmission of any signal through the sympathetic system: pre-ganglionic and post-ganglionic. 2.2 Relationship with the parasympathetic nervous system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
